GPS
GPS is a satellite-based global navigation system (GNNS) that provides geolocation data and enables positions to be fixed to within a few centimeters (when using differential GPS) or meters.
GPS operates through a network of 32 satellites (28 operational and 4 backups) in orbit around the globe, at 23,200 km, with synchronized paths to cover the entire surface of the Earth. To determine a position, the receiver automatically locates at least three satellites (within the network), from which it receives signals indicating the identification and clock time of each of them. Based on these signals, the apparatus synchronizes the GPS clock and calculates how much time the signals take to reach the device. This way, the distance to the satellite is measured through triangulation (inverse trilateral method). Once the distances are known, the relative position with respect to the three satellites can be easily determined. In addition, if you know the coordinates, or the position of each of these through the signals they broadcast, you can get an accurate position from the measuring point. Precise accuracy is achieved thanks to the GPS clock, which is similar to the atomic clocks on board the satellites.
This service reads from a source with GPS data and launch a TCP server to make it available to any client connected.
Configuration
First of all, it is necessary to configure the GPS serial port. You can do so by using this command:
set controllers gps gps0
“gps0” is just the name to the serial port “/dev/gps0” so if there was two GNSS modules (both connected to serial ports), there would be a “gps1”.
Once this step is made, you can run your GPS service using that serial port as source.
set service gps gps0 source gps0
In the command above, the first “gps0” is just an id given by the user but the second “gps0” is the name of the gps controller. This means that is possible to have multiples “instances” running of the gps service with multiples sources each instance. Here are the settings you can set when configuring GPS in your system:
geofence: used for geofencing. Works with user-defined zones.
log-level: Set the log-level for all GPS related logs. By default is error.
source: select the GPS (GNSS) controller to use.
tcp-enable: enable tcp remote connection.
tcp-port: configure listen tcp port.
Geofencing
Geofencing is a sub-service designed to control the behavior of the device using the logic of the advisors and alarms. The state of the alarms depends on whether the location of the device is inside or outside of a given zone.
zone: A zone is a geographical area delimited by two coordinate-defined points. This lets you define zones delimited by two latitude and two longitude values (similar to a rectangle):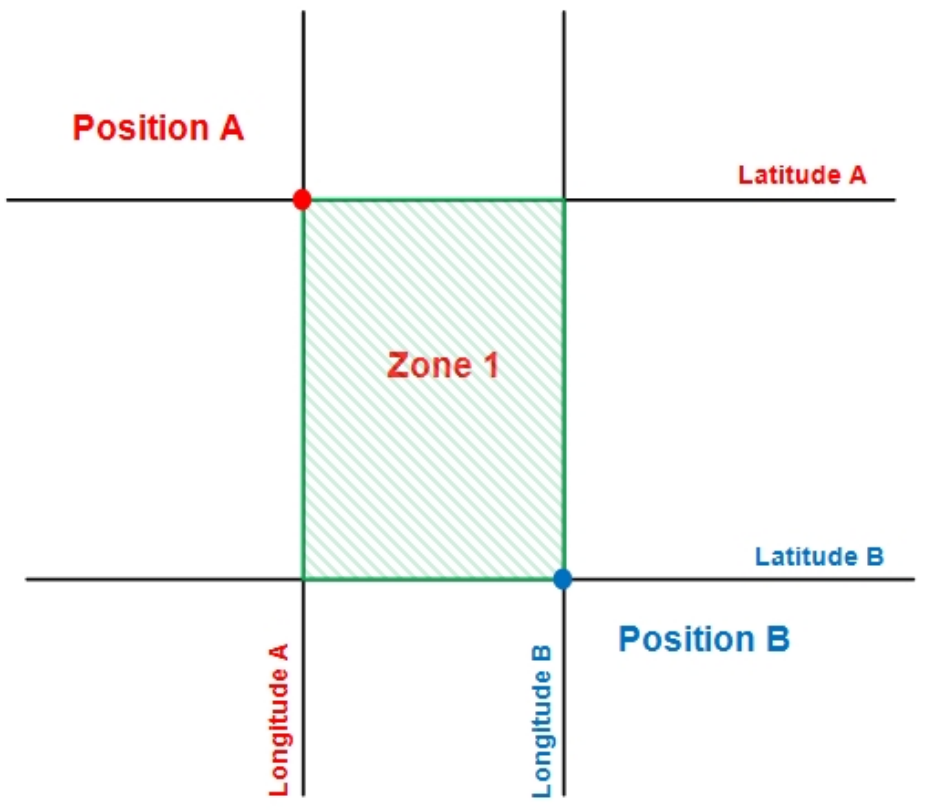
For example, to create a zone with two points which have these coordinates:
Position A: 40º36.4740N, 3º43.4280W
Position B: 40º37.0740N, 3º44.0280W
These commands are used:
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 latitude 40º36.4740N to 40º37.0740N set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 longitude 3º43.4280W to 3º44.0280W
Once a zone is defined, you can set different options for each zone:
alarm: name of the alarm. This option is required.
coverage-fail-state: state on coverage failure. If it should change to inside/outside immediately or after a certain time.
coverage-fail-state-time: state timer on coverage failure.
initial-state: initial state at power ON. If it should change to inside/outside immediately or after a certain time.
initial-state-time: initial state timer.
latitude: latitude range of the zone, for example 45°30.5N. Use º or ° as degrees symbol. This option is required.
longitude: longitude range of the zone, for example 123°45.67E. Use º or ° as degrees symbol. This option is required.
time-to-false: time to validate OUT of zone when having coverage.
time-to-true: time to validate IN of zone when having coverage.
A basic configuration can be:
set system alarm ZONE1
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 coverage-fail-state true-time-false
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 coverage-fail-state-time '00:03:00'
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 initial-state false-time-true
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 initial-state-time '00:06:30'
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 latitude 40º35.0000N to 40º37.0740N
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 longitude 3º50.4280W to 3º30.0280W
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 alarm ZONE1
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 time-to-true '00:02:00'
set service gps gps0 geofence zone 1 time-to-false '00:02:00'
Examples
This example show how to set a TCP Server open to external clients in port 2948 with a geofence sub-service.
The following commands are needed to achieved it:
set controllers gps gps0
set service gps gps0 source gps0
set service gps gps0 tcp-enable
set service gps gps0 tcp-port 2948
set service gps gps0 geofence
Example:
admin@DUT0$ show system connections listening | grep "2948"
tcp LISTEN 0 5 0.0.0.0:2948 0.0.0.0:*
tcp LISTEN 0 5 [::]:2948 [::]:*
admin@DUT0$ service gps gps0 status tcp
Remote GPS state for instance gps0: OPEN port:2948
TCP Client: 1
IP Addr:127.0.0.1
Port:37976
Note
Geofencing sub-service is just another TCP client.
Monitoring commands
The gps has multiple monitoring commands. Some of them show information about the status of the service and others about the GPS data. They are available under the path:
service gps <id> <operation>
The available operations are:
monitor: launch an interactive shell to see real-time data as well as statistical information.
position: get the current position.
statistical: Show GPS statistic data.
status: to see the status of the zones or of the clients connected to the server.
Example:
admin@DUT0$ service gps gps0 monitor
tcp://osdx:2948 NMEA0183>
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│Time: 2025-03-10T14:48:48.000Z Lat: 40 35.476050' N Lon: 3 42.467480' W │
└───────────────────────────────── Cooked TPV ─────────────────────────────────┘
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ PSTMDRSENMSG PSTMANTENNASTATUS GPRMC GPGGA GPVTG GNGSA GPGSV GLGSV GA... │
└───────────────────────────────── Sentences ──────────────────────────────────┘
┌───────────────────────┌─────────────────────────┌────────────────────────────┐
│ SVID PRN Az El SN HU│Time: 144848.000 │Time: 144848.000 │
│GP 2 2 270 50 28 Y│Latitude: 4035.47605 N │Latitude: 4035.47605 │
│GP 8 8 321 65 34 Y│Longitude: 00342.46748 W │Longitude: 00342.46748 │
│GP 10 10 71 54 25 Y│Speed: 0.1 │Altitude: 747.26 │
│GP 23 23 40 19 36 Y│Course: 191.0 │Quality: 1 Sats: 14 │
│GP 27 27 85 68 27 Y│Status: A FAA:A │HDOP: 0.9 │
│GP 32 32 117 9 18 Y│MagVar: │Geoid: 51.7 │
│GL 5 69 27 13 33 Y└───────── RMC ───────────└─────────── GGA ────────────┘
│GL 12 76 274 48 23 Y┌─────────────────────────┌────────────────────────────┐
│GL 13 77 325 23 25 Y│Mode: A3 Sats: 2 8 10 + │UTC: RMS: │
│GL 21 85 44 41 40 Y│DOP H=0.9 V=1.2 P=1.5 │MAJ: MIN: │
│GA 13 313 50 35 36 Y│TOFF: -29852.130036400 │ORI: LAT: │
│GA 31 331 315 27 36 Y│PPS: N/A │LON: ALT: │
└───v──── GSV ──────────└────── GSA + PPS ────────└─────────── GST ────────────┘
Command Summary
Configuration commands
service gps <id> geofence zone <u32> coverage-fail-state <txt>service gps <id> geofence zone <u32> coverage-fail-state-time <txt>service gps <id> geofence zone <u32> initial-state-time <txt>service gps <id> geofence zone <u32> latitude <txt> to <txt>service gps <id> geofence zone <u32> longitude <txt> to <txt>